Agriculture is essential to our society, and fertilizers are crucial in improving crop yield and quality. Familiarizing oneself with the different types of fertilizers can aid you in choosing the appropriate one for specific crops and soil conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the most commonly used fertilizers in agriculture, their properties, and how they contribute to the growth of various crops. So, in the end, you will not question what are the most common fertilizers used in agriculture.
The Most Common Fertilizers Used in Agriculture
These are just a few examples of the most common fertilizers used in agriculture. Each type of fertilizer plays a unique role in supporting plant growth and crop development, and understanding their characteristics can significantly impact the success of agricultural practices.
Nitrogen Fertilizers
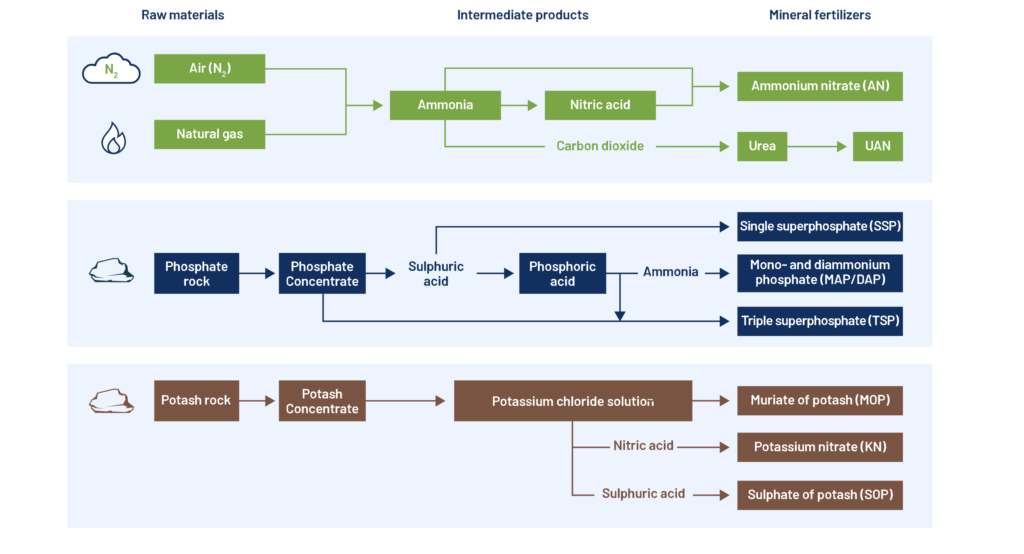
Nitrogen is one of the most common fertilizers used in wide farming. Nitrogen is one of the primary macronutrients for plant growth and is essential for forming proteins, chlorophyll, and other important plant compounds. It plays a crucial role in photosynthesis, enabling plants to convert sunlight into energy. Nitrogen fertilizers are widely used to promote the growth of leafy and green crops. These fertilizers come in various forms, including urea, ammonium nitrate, and ammonium sulfate, and are commonly applied to the soil or foliage of plants. When applied, nitrogen fertilizers dissolve in soil moisture and are absorbed by plant roots or leaves. Nitrogen fertilizers are popular because they can significantly increase crop yields and improve plant quality. However, excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers can lead to environmental problems such as water pollution and soil degradation.
Phosphorus Fertilizers
The most common source of phosphorus for plants is through fertilizers, such as superphosphate and triple superphosphate, which contain soluble forms of phosphorus that plant roots can easily absorb. These fertilizers are particularly beneficial for crops that require strong root systems, such as fruits and vegetables, as phosphorus promotes vigorous root growth and enhances plant resistance to stress, diseases, and pests. However, excessive use of phosphorus fertilizers can lead to environmental problems, such as water pollution and eutrophication, and it is important to apply them judiciously based on soil test results and crop requirements.
Potassium Fertilizers
Potassium is particularly important for developing fruits and seeds, increasing their size, quality, and flavor. Plants that receive adequate potassium fertilization also exhibit strong resistance to pests and diseases, as this nutrient helps to strengthen the cell walls and facilitate the transport of nutrients within the plant.
Fertilizers that provide potassium, such as potassium chloride and potassium sulfate, are highly recommended for improving crop yields and quality. Potassium chloride is a common source of potassium, containing 60-62% K2O, while potassium sulfate is a more expensive option that contains 50% K2O and 18% sulfur. Both fertilizers are typically applied to the soil, where they dissolve and release potassium ions that the plant roots can take up. You can help your crops thrive and produce healthy, flavorful, and nutritious fruits and vegetables by ensuring sufficient potassium levels in the soil.
Production of main fertilizer products, International Fertilizer Association, www.fertilizer.org
The Importance of Micronutrient Fertilizers
Did you know that while nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium fertilizers are important for plant growth, micronutrient fertilizers are also crucial for optimal plant health? These fertilizers contain trace elements like iron, zinc, copper, and manganese, essential for specific plant metabolic processes. Micronutrient deficiencies can significantly impact crop yield and quality, resulting in yellowing leaves, stunted growth, and reduced fruit production. By understanding the role of micronutrient fertilizers, you can take the necessary steps to address these deficiencies and ensure that plants are healthy and happy.
Different Types of Slow-Release Fertilizers
In addition to conventional fertilizers, slow-release fertilizers have gained popularity in modern agriculture and are considered common fertilizers used in agriculture. These fertilizers provide nutrients to plants over an extended period, reducing the risk of nutrient leaching and promoting more efficient crop uptake.
Different slow-release fertilizers are available, including polymer-coated fertilizers, sulfur-coated urea, and organic-based fertilizers. Each type offers unique benefits, such as prolonged nutrient release and improved soil fertility. By incorporating slow-release fertilizers into your agricultural practices, you can optimize nutrient utilization and minimize environmental impact. So, to help your plants thrive while being mindful of the environment, consider using slow-release fertilizers in your agricultural practices.
How to Optimize the Fertilizer Process and Use Them Properly
Applying fertilizers is crucial for optimal plant growth and yield in agriculture. Proper usage of fertilizers is necessary, including adhering to the recommended dosage. However, ensuring that the fertilizer is accurately distributed and sprayed for each plant can be challenging. How can I be certain that each plant receives the appropriate amount of fertilizer?
Terra Agri has led innovative fertilizer spraying projects in Indonesia and Malaysia, bringing about a revolution in sustainable agriculture practices in the region. By digitizing the fertilizing process, Terra Agri has reduced human error and ensured fertilizers’ precise and efficient application. This technological advancement has significantly improved crop yields and quality while minimizing environmental impact.
By tracking the fertilizing process through digital platforms, you can monitor the effectiveness of their fertilizer application and make informed decisions to enhance crop health and productivity. Terra Agri’s successful initiatives are exemplary models for integrating modern technology into agricultural practices, promoting sustainable and efficient crop cultivation.

